Introduction
Human Resource Management (HRM) is the backbone of every successful organization. It’s the strategic process of managing a company’s most valuable asset — its people. HRM ensures employees are recruited, trained, motivated, and retained to maximize productivity.
Beyond hiring and firing, HRM creates a positive work culture, aligns employees with business goals, and drives organizational growth.
What is Human Resource Management (HRM)?
Definition:
Human Resource Management is the process of recruiting, developing, managing, and retaining employees to achieve organizational objectives. HRM ensures employees grow in their careers, improve performance, and remain motivated.
Simple Definition: HRM = Managing People at Work.
It’s all about hiring the right talent, helping them grow, keeping them engaged, and ensuring they perform at their best.

Objectives of Human Resource Management
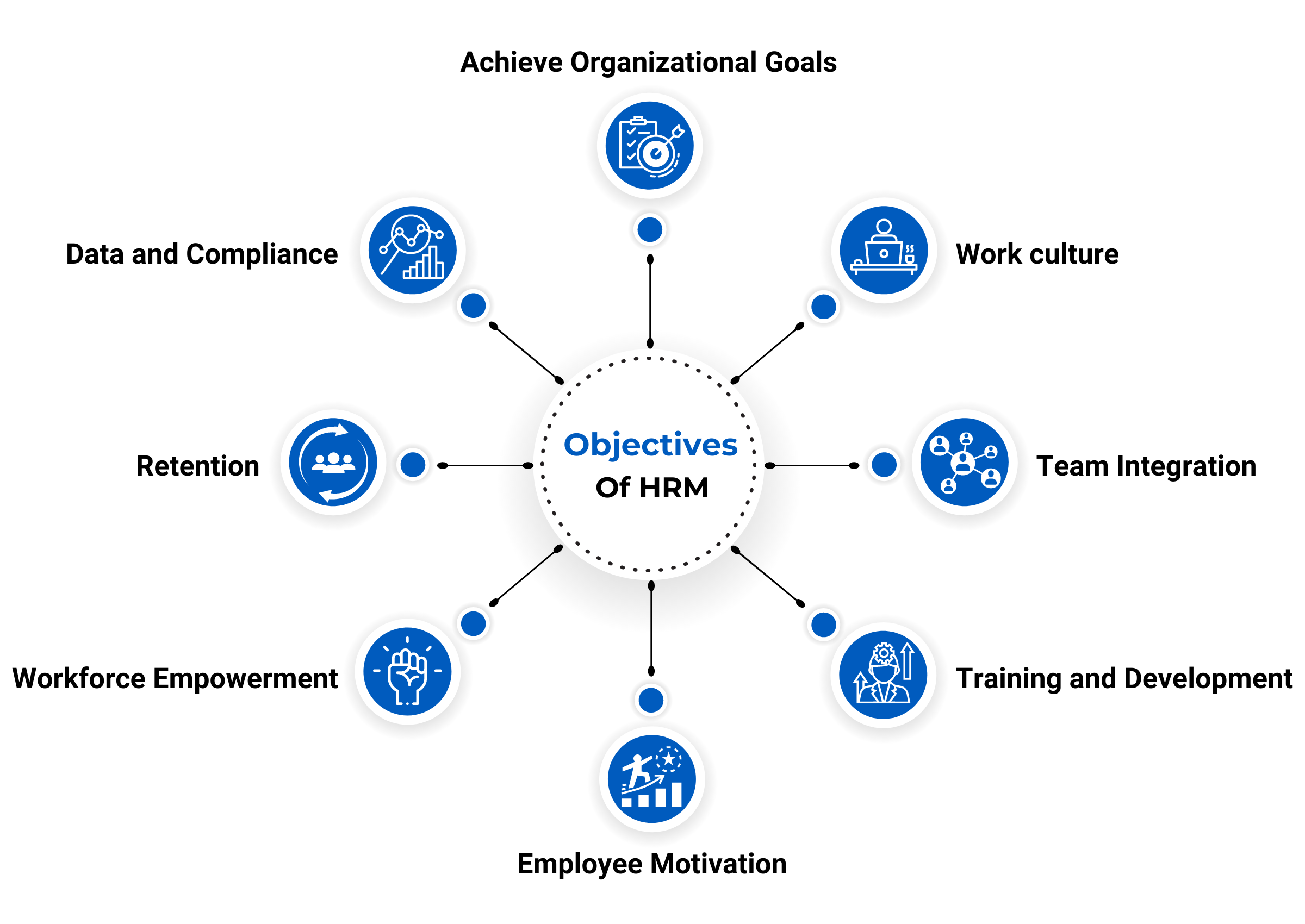
1. Hire the Right People
HR ensures employees have the right skills and fit the company culture. This includes:
-
Clear job descriptions
-
Structured interviews and assessments
-
Diversity and inclusion initiatives
-
Reducing hiring mistakes
Benefit: Right talent reduces training costs, improves productivity, and strengthens team synergy.
2. Employee Development
Investing in employees boosts performance and loyalty:
-
Training programs, workshops, and e-learning
-
Mentorship and career advancement
-
Cross-functional skill development
-
Staying updated with industry trends
Benefit: Confident, skilled employees contribute more to organizational success.
3. Performance Optimization
HR aligns individual performance with organizational goals:
-
Setting clear objectives
-
Regular performance reviews
-
Incentives and recognition
-
Addressing performance gaps
Benefit: Higher output, improved quality, and satisfied customers.
4. Retention & Engagement
Keeping employees is as crucial as hiring them:
-
Positive workplace culture
-
Competitive compensation and benefits
-
Open communication
-
Team-building activities
Benefit: Engaged employees stay longer, reducing turnover and recruitment costs.
5. Compliance
HR ensures adherence to labor laws, safety regulations, and workplace policies:
-
Accurate records and contracts
-
Anti-discrimination policies
-
Workplace safety
Benefit: Protects the organization legally and promotes fairness.
6. Workplace Harmony
Collaboration and respect boost organizational efficiency:
-
Diversity, equity, and inclusion
-
Conflict resolution
-
Team collaboration
-
Employee well-being programs
Benefit: Reduced stress, increased motivation, and higher productivity.
Functions of Human Resource Management
1. Recruitment & Selection
Recruitment and selection is the process of finding, attracting, and hiring the right people for the right jobs.
Key Activities:
-
Job Analysis: Identify the duties, responsibilities, and skills needed for the role.
-
Job Posting: Advertise openings on job boards, company websites, and social media.
-
Screening & Shortlisting: Review applications and shortlist suitable candidates.
-
Interviews & Assessments: Evaluate candidates through structured interviews, skill tests, or personality assessments.
-
Final Selection: Offer the job to the most suitable candidate.
Why It’s Important:
Hiring the right people ensures high productivity, reduces turnover, and builds a strong company culture.
Example:
An IT company hiring a software developer will post the job on LinkedIn, conduct coding tests, and interview candidates before selecting the best fit.
2. Training & Development
Training & development ensures employees gain the knowledge and skills they need to perform their jobs effectively and grow in their careers.
Key Activities:
-
Onboarding Programs: Introduce new hires to company policies, culture, and processes.
-
Skill Development Workshops: Train employees on technical or soft skills.
-
Leadership Programs: Prepare employees for managerial roles.
-
Continuous Learning: Offer online courses, seminars, and certifications.
Why It’s Important:
A well-trained workforce is more efficient, confident, and motivated. It also reduces errors and improves customer satisfaction.
Example:
A retail company might train cashiers on customer service skills and inventory management software.
3. Performance Management
Performance management involves monitoring, evaluating, and improving employee performance to achieve organizational goals.
Key Activities:
-
Goal Setting: Define clear performance objectives for each employee.
-
Regular Feedback: Provide constructive feedback to help employees improve.
-
Performance Appraisals: Conduct formal reviews to measure achievements.
-
Recognition & Rewards: Appreciate high performers with bonuses, promotions, or awards.
Why It’s Important:
It ensures that employees stay aligned with business objectives and continue to improve their skills and efficiency.
Example:
A sales manager tracking monthly sales targets and rewarding top-performing sales executives.
4. Compensation & Benefits
Compensation & benefits include all the rewards an employee receives for their work — salary, bonuses, and non-monetary perks.
Key Activities:
-
Salary Structure Design: Create fair and competitive pay packages.
-
Incentives & Bonuses: Motivate employees to perform better.
-
Health & Wellness Benefits: Provide health insurance, gym memberships, or counseling services.
-
Retirement Plans: Offer provident funds, pensions, or retirement savings schemes.
Why It’s Important:
Fair and attractive compensation motivates employees, reduces turnover, and attracts top talent.
Example:
An MNC offering a base salary, performance bonus, free health check-ups, and paid vacations.
5. Employee Relations
Employee relations focus on maintaining a positive and productive work environment.
Key Activities:
-
Conflict Resolution: Address disputes between employees or between employees and management.
-
Engagement Programs: Organize team-building activities, events, or surveys.
-
Communication Channels: Maintain open communication between management and employees.
-
Employee Support: Provide help during personal or professional challenges.
Why It’s Important:
Strong employee relations improve job satisfaction, reduce stress, and boost overall workplace morale.
Example:
A company organizing regular “Town Hall” meetings to discuss updates and take employee feedback.
6. Compliance & Legal Responsibilities
Compliance means ensuring that the organization follows all labor laws, workplace safety rules, and ethical business standards.
Key Activities:
-
Labor Law Compliance: Follow regulations regarding wages, working hours, and overtime.
-
Workplace Safety: Provide safe equipment, proper training, and emergency protocols.
-
Equal Opportunity Policies: Prevent discrimination in hiring and promotion.
-
Ethical Business Practices: Maintain transparency and fairness in all HR decisions.
Why It’s Important:
Non-compliance can result in legal penalties, reputational damage, and employee dissatisfaction.
Example:
An HR team ensuring that employee contracts meet the requirements of the country’s labor laws and providing mandatory safety training for factory workers.
Importance of Human Resource Management (HRM)
Human Resource Management is not just about hiring people — it’s about ensuring that employees and the organization grow together. A strong HR system improves productivity, builds a positive work culture, and drives long-term success.
1. Increases Productivity
When employees are well-trained, motivated, and placed in the right roles, they perform better.
-
HR ensures that employees have the skills, resources, and support they need.
-
Through training programs, performance appraisals, and feedback sessions, HR helps employees improve efficiency.
-
Motivated employees take ownership of their work, leading to higher output and better results.
2. Reduces Turnover
High employee turnover is expensive — it affects team morale and increases recruitment costs.
-
HR focuses on employee satisfaction, career growth, and work-life balance, reducing the chances of people leaving.
-
Initiatives like recognition programs, wellness benefits, and career development keep employees engaged and loyal.
-
A low turnover rate helps maintain continuity and stability within the organization.
3. Builds a Strong Company Brand
A company’s reputation as a great place to work depends heavily on HR practices.
-
Positive work culture, fair policies, and opportunities for growth make the organization attractive to top talent.
-
Happy employees often act as brand ambassadors, recommending the company to others.
-
Strong employer branding also helps in attracting high-quality candidates during recruitment.
4. Aligns People with Business Goals
For a company to succeed, everyone must work toward the same objectives.
-
HR ensures that employees understand the company’s mission, vision, and strategic goals.
-
Through performance management systems, HR aligns individual KPIs with organizational goals.
-
This alignment boosts efficiency, eliminates confusion, and ensures that every effort contributes to business success.
5. Promotes Diversity and Inclusion
Workplaces thrive when people from different backgrounds, cultures, and experiences work together.
-
HR plays a vital role in creating equal opportunities for all employees.
-
Diversity policies encourage hiring from a wide talent pool, while inclusion programs ensure that everyone feels valued.
-
This leads to more creativity, better problem-solving, and a healthier workplace culture.

Types of Human Resource Management
Human Resource Management has evolved over time, moving from simple administrative work to becoming a strategic partner in business growth. Broadly, HRM can be divided into three main types:
1. Traditional HRM
Focus: Administrative and operational tasks.
In its early form, HRM was mainly about handling routine employee-related processes. The focus was on record-keeping, compliance, and ensuring the basic needs of the workforce were met. This type of HRM plays more of a supporting role rather than directly influencing company strategy.
Key Points:
-
Administrative focus: Managing payroll, attendance, and employee records.
-
Recruitment & hiring: Filling open positions as they come up without a long-term manpower plan.
-
Policy enforcement: Ensuring rules and workplace regulations are followed.
-
Problem-solving: Addressing employee grievances and maintaining discipline.
Example:
An HR department that mainly deals with processing salaries, tracking leave, and handling hiring paperwork without actively shaping company policies.
2. Strategic HRM
Focus: Aligning HR policies with long-term business goals.
Strategic HRM (SHRM) moves beyond day-to-day administration. It views employees as valuable assets whose skills, motivation, and performance directly influence the company’s success. HR professionals in this model actively participate in business planning and align human resource policies with the organization’s vision.
Key Characteristics:
-
Workforce planning: Hiring and training employees based on future business needs.
-
Talent management: Building strong career paths and leadership pipelines.
-
Performance alignment: Ensuring individual goals match organizational objectives.
-
Proactive role: Involvement in decision-making at the executive level.
Example:
An HR team that collaborates with top management to design a five-year hiring plan for entering a new market, ensuring the right talent is ready when needed.
3. Modern HRM
Focus: Technology-driven, employee-centric approach.
Modern HRM combines the strengths of both traditional and strategic HRM but adds technology, data analytics, and employee engagement strategies to the mix. It’s about creating a positive work culture, improving employee experience, and using tools to make data-driven HR decisions.
Key Characteristics:
-
HR technology: Using HR software (HRIS), AI-based recruitment tools, and digital onboarding.
-
Data analytics: Tracking employee performance, engagement, and retention metrics.
-
Employee well-being: Focusing on work-life balance, mental health, and inclusivity.
-
Continuous learning: Promoting upskilling and reskilling to meet industry changes.
Example:
A company that uses AI to screen resumes, offers online training modules for employees, conducts pulse surveys for engagement, and uses analytics to predict turnover.
Future of Human Resource Management (HRM)
The workplace is evolving rapidly, and so is Human Resource Management. Advancements in technology, changing employee expectations, and a focus on workplace well-being are shaping the future of HRM. Here are the key trends to watch:
1. Remote & Hybrid Work – More Flexibility for Employees
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the shift toward remote and hybrid work models, and they’re here to stay.
-
HR will focus on managing distributed teams, ensuring productivity while supporting work-life balance.
-
New policies for remote work, such as flexible hours and virtual collaboration tools, will be standard.
-
Organizations will need to invest in digital workplace infrastructure to keep employees connected and engaged.
2. AI Recruitment Tools – Faster Candidate Screening
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming recruitment.
-
AI-powered software can scan thousands of resumes in minutes, shortlist candidates, and even conduct initial screening interviews.
-
This allows HR professionals to focus on relationship-building and strategic decision-making rather than repetitive tasks.
-
Predictive analytics can also help in hiring the right talent based on skills, cultural fit, and performance potential.
3. Employee Wellness Programs – Focus on Mental Health
Employee well-being is no longer limited to physical health.
-
HR will prioritize mental health support, offering counseling services, stress management workshops, and mindfulness programs.
-
Flexible schedules, wellness allowances, and burnout prevention initiatives will become more common.
-
A strong wellness program helps improve productivity, morale, and retention.
4. Diversity & Inclusion Initiatives – Building Fair, Respectful Workplaces
Future HR strategies will emphasize creating workplaces where everyone feels valued.
-
HR will implement unbiased recruitment processes to attract diverse talent.
-
Ongoing training on cultural sensitivity, gender equality, and inclusion will become the norm.
-
Companies that embrace diversity will benefit from greater creativity, innovation, and problem-solving skills.
Conclusion
Human Resource Management is more than just hiring — it’s about developing, supporting, and motivating employees so they can contribute to business success.
In today’s fast-changing work environment, effective HRM is the key to building strong, happy, and productive teams.
FAQs
1. What is the main role of HRM?
To manage people effectively so they can contribute to the success of the organization.
2. What are the key functions of HRM?
Recruitment, training, performance management, compensation, and employee relations.
3. Is HRM only for large companies?
No, even small businesses benefit from proper HRM practices.
4. How is HRM changing?
It’s becoming more technology-driven, people-focused, and strategic.