Recruitment is one of the most critical functions of Human Resource Management (HRM), as it ensures that the right people with the right skills are hired at the right time to meet organizational needs. A streamlined recruitment process not only helps in finding candidates who can perform their job responsibilities effectively but also ensures they fit into the organizational culture and work well with existing employees. Moreover, a well-structured recruitment process plays a vital role in filling open positions efficiently, building a strong employer brand, and improving overall employee retention.

What is Recruitment?
Recruitment is a process of finding and attracting the potential resources for filling up the vacant positions in an organization. It sources the candidates with the abilities and attitude, which are required for achieving the objectives of an organization.
What Is the Recruitment Process?
The recruitment process is the systematic approach organizations use to identify, attract, evaluate, and hire the best-suited candidates for job openings. It involves steps such as identifying hiring needs, creating job descriptions, sourcing candidates, screening applications, conducting interviews, selecting the right talent, and finally onboarding them into the organization.
Why is Recruitment Important?
-
Ensures skilled and qualified employees join the organization.
-
Reduces turnover by selecting the right cultural fit.
-
Improves company productivity and growth.
-
Builds a strong employer brand in the market.
Importance Of A Recruitment Process
A good recruitment process follows a step-by-step approach to identifying and hiring qualified candidates who can contribute to business growth. It not only ensures that the right talent is selected but also supports long-term organizational success. Below are some key reasons why a structured recruitment process is important:
-
Attracts the Right Talent – Helps bring in skilled and qualified candidates suitable for the role.
-
Ensures Cultural Fit – Selects employees who align with the organization’s values and work culture.
-
Reduces Employee Turnover – Hiring the right people lowers attrition rates.
-
Improves Productivity – Ensures positions are filled with capable individuals who can perform effectively.
-
Builds Employer Brand – A smooth recruitment experience creates a positive impression of the company.
-
Saves Time and Resources – Streamlined hiring reduces unnecessary delays and costs.
-
Promotes Fairness and Transparency – Ensures equal opportunities and compliance with labor laws.
-
Supports Business Growth – Provides the right talent at the right time to meet organizational goals.
Step-by-Step Recruitment Process
A recruitment process typically follows eight steps. Here are the stages of the recruitment process.
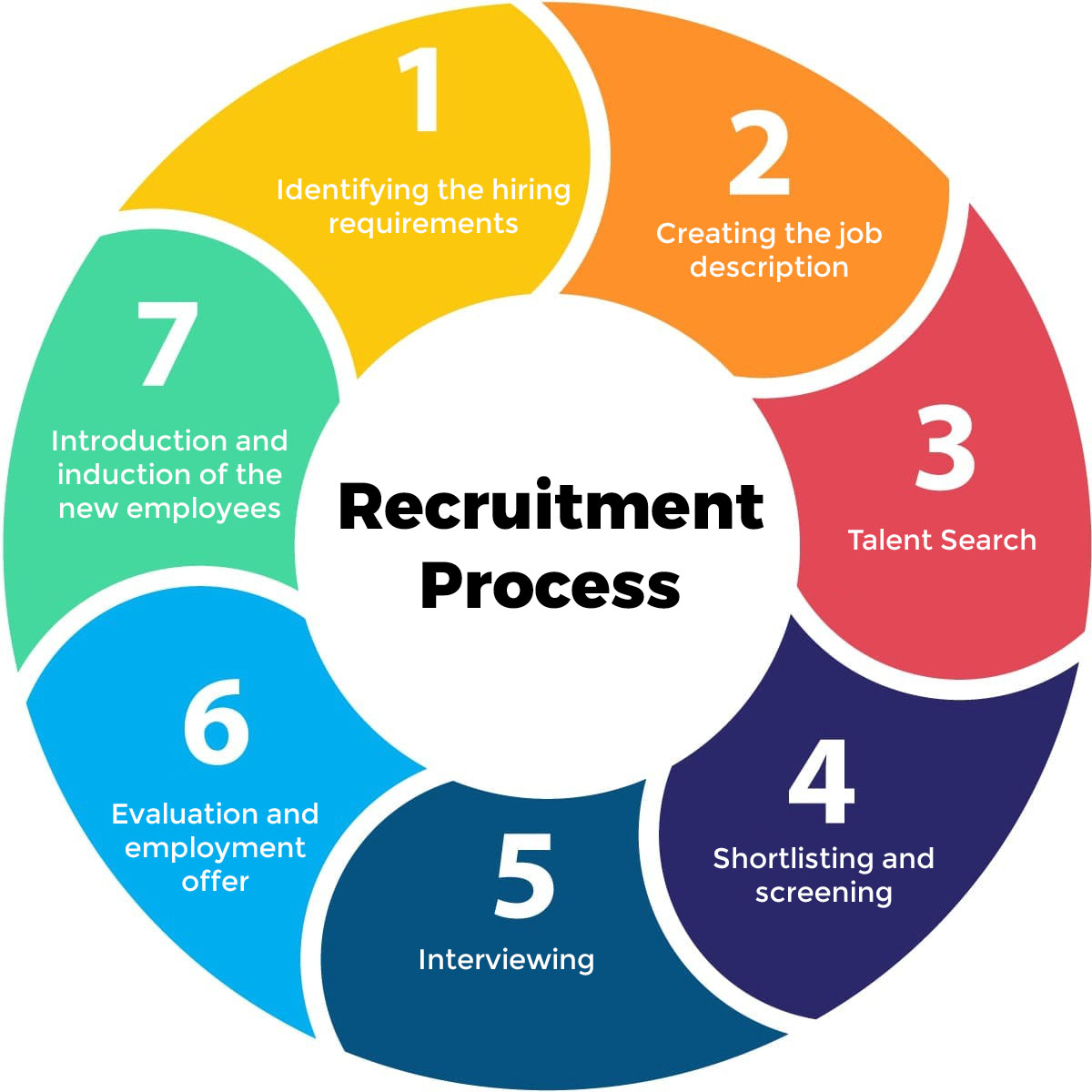
1. Identify vacancies and hiring needs
The first and foremost process of recruitment plan is identifying the vacancy. This process begins with receiving the requisition for recruitments from different department of the organization to the HR Department, which contains:
- Number of posts to be filled
- Number of positions
- Duties and responsibilities to be performed
- Qualification and experience required
When a vacancy is identified, it the responsibility of the sourcing manager to ascertain whether the position is required or not, permanent or temporary, full-time or part-time, etc. These parameters should be evaluated before commencing recruitment. Proper identifying, planning and evaluating leads to hiring of the right resource for the team and the organization.
Example: If sales are growing, the company may need additional sales executives.
2. Creating a Job Description (JD)
Job description is an important document, which is descriptive in nature and contains the final statement of the job analysis. This description is very important for a successful recruitment process.
Job description provides information about the scope of job roles, responsibilities and the positioning of the job in the organization. And this data gives the employer and the organization a clear idea of what an employee must do to meet the requirement of his job responsibilities.
Job description is generated for fulfilling the following processes:
- Classification and ranking of jobs
- Placing and orientation of new resources
- Promotions and transfers
- Describing the career path
- Future development of work standards
A job description provides information on the following elements:
- Job Title / Job Identification / Organization
- Job location
- Summary of job
- Job duties
- Machines, Materials and Equipment
- Process of Supervision
- Working Conditions
- Health Hazards
Example: If a company plans to hire a Digital Marketing Executive, the HR team will create a job description that clearly defines the role. The JD may include responsibilities like managing social media campaigns, running online advertisements, analyzing performance metrics, and preparing marketing reports. It will also list required qualifications such as a bachelor’s degree in marketing, knowledge of SEO/SEM, and strong communication skills.
3. Sourcing Candidates
Sourcing candidates is the process of identifying and attracting potential job seekers to apply for open positions within an organization. It focuses on building a pool of qualified applicants by reaching out through different channels such as job portals, social media, company websites, employee referrals, recruitment agencies, and campus placements. Effective candidate sourcing ensures that the organization has access to the best talent available in the market, saving time in the hiring process and increasing the chances of finding the right fit for the role.
Once your compelling job description is ready, it’s time to go fishing for top talent! There are two main ways to find potential hires: internally, through your employee network, and externally, leveraging the wider job market.
Internal Sources:
Internal sources of recruitment refer to hiring employees within the organization through:
- Promotions
- Transfers
- Former Employees
- Internal Advertisements (Job Posting).
- Employee Referrals
- Previous Applicants
External Sources:
External sources of recruitment refer to hiring employees outside the organization through:
- Direct Recruitment
- Employment Exchanges
- Employment Agencies
- Professional Associations
- Campus Recruitment
- Word of Mouth
Example: Suppose a company is looking to hire a Software Developer. The HR team begins sourcing candidates by posting the job on LinkedIn, Naukri, and Indeed to attract active job seekers. At the same time, they reach out to their professional network and ask current employees for referrals. To expand the talent pool further, they collaborate with a recruitment agency that specializes in IT roles. The HR team also connects with potential candidates on social media groups, attends a local job fair, and participates in campus placement drives to engage fresh graduates. By using multiple sourcing methods, the company ensures a diverse pool of qualified applicants to choose from.
4. Screening and Shortlisting
Screening starts after completion of the process of sourcing the candidates. Screening is the process of filtering the applications of the candidates for further selection process.
Screening is an integral part of recruitment process that helps in removing unqualified or irrelevant candidates, which were received through sourcing. The screening process of recruitment consists of three steps:
Reviewing of Resumes and Cover Letters
Reviewing is the first step of screening candidates. In this process, the resumes of the candidates are reviewed and checked for the candidates’ education, work experience, and overall background matching the requirement of the job.
While reviewing the resumes, an HR executive must keep the following points in mind, to ensure better screening of the potential candidates:
Example: A company receives 300 applications for the role of Sales Executive. The HR team first uses an Applicant Tracking System (ATS) to filter candidates who meet the minimum qualifications, such as a bachelor’s degree and 2+ years of sales experience. Next, they manually review the shortlisted resumes to check for specific skills like communication, negotiation, and client handling. Finally, they narrow the list down to 20 candidates who are best suited for the role and invite them for the first round of interviews.
5. Conducting Interviews
Interviews help assess candidates beyond their resumes. Types of interviews include:
- Telephonic/Video Screening – Conducting telephonic or video interviews is the second step of screening candidates. In this process, after the resumes are screened, the candidates are contacted through phone or video by the hiring manager.
- Technical Interview – A technical interview is conducted to assess a candidate’s job-specific knowledge, problem-solving ability, and practical skills related to the role. It often includes technical questions, case studies, coding tests, or task-based assessments to evaluate whether the candidate can perform the core responsibilities of the job effectively.
- HR Interview – Conducted by the HR team to assess the candidate’s personality, cultural fit, salary expectations, and overall suitability for the organization.
- Panel Interview – An interview where multiple interviewers (managers, HR, or senior team members) evaluate a candidate together to get diverse perspectives before making a hiring decision.
Example: A company is hiring a Marketing Executive. After shortlisting candidates, the HR team schedules the first round as a telephonic interview to check communication skills and basic knowledge. The selected candidates then move to a technical interview, where they are asked to create a sample social media campaign and analyze marketing data. Next, the shortlisted applicants attend an HR interview to discuss their career goals, salary expectations, and cultural fit. Finally, the top three candidates are invited for a panel interview with the marketing manager, HR head, and senior executives. Based on their performance in all stages, the company selects the best candidate for the role.
6. Candidate Evaluation and Selection
After the interview rounds, recruiters and hiring managers carefully evaluate candidates on multiple dimensions to ensure the best fit for the role and organization. Key evaluation factors include:
-
Technical Skills – Assessing whether the candidate has the required job-related knowledge and expertise.
-
Problem-Solving Abilities – Evaluating how effectively the candidate can analyze issues, think critically, and provide practical solutions.
-
Soft Skills – Reviewing essential interpersonal skills such as communication, teamwork, adaptability, and leadership qualities.
-
Cultural Alignment – Determining whether the candidate’s values, attitude, and work style align with the organization’s culture.
Example:
After completing all interview rounds for the Marketing Executive role, the HR team and hiring manager evaluate each candidate based on communication, technical skills, cultural fit, and overall performance. They compare interview feedback, test results, and panel impressions to identify the strongest applicant. Finally, the company selects the most suitable candidate to move forward with the job offer.
7. Job Offer & Negotiation
Once the best-fit candidate is finalized, HR extends a formal job offer letter. This document clearly outlines the key details of employment, including:
-
Role and Responsibilities – A clear description of the position and expectations.
-
Compensation Package – Salary details, incentives, and other financial components.
-
Benefits and Perks – Information about health insurance, retirement plans, paid leave, and additional perks.
-
Joining Date – The official start date of employment.
In this stage, candidates may also negotiate aspects such as salary, flexible working options, or additional benefits. A transparent and fair negotiation process helps build trust and ensures both parties enter into the agreement with clarity and confidence.
Example:
Once the company finalizes the candidate for the Marketing Executive role, the HR team extends a formal job offer, outlining salary, benefits, and joining date. The candidate reviews the offer and discusses aspects like compensation, work flexibility, and growth opportunities. After a brief negotiation, both parties agree on the terms, and the candidate officially accepts the offer.
8. Onboarding the New Hire
Onboarding is a crucial step that helps new employees transition smoothly into the organization and become productive quickly. A structured onboarding program creates a positive first impression and sets the foundation for long-term engagement. Key activities include:
-
Orientation Sessions – Introducing company policies, values, and culture.
-
Team Introductions – Helping the new hire connect with colleagues and build relationships.
-
Training on Tools and Processes – Providing hands-on guidance to perform their role effectively.
-
Documentation & Compliance – Completing necessary HR forms, payroll details, and legal formalities.
A strong onboarding process not only enhances employee satisfaction but also improves retention by making employees feel welcomed, supported, and aligned with organizational goals.
Example:
After selecting a Marketing Executive, the company ensures a smooth onboarding process. Before joining, the HR team shares the welcome email, company policies, and required documents. On the first day, the new hire is introduced to the team, given an orientation about the company’s culture, and provided with system access. During the first week, the manager assigns a small project and pairs the new employee with a mentor to ease the transition. Over the next few weeks, regular check-ins and feedback sessions help the employee settle in. At the end of three months, a performance review is conducted to discuss progress and future goals.
Read more: Recruitment process
Conclusion
The recruitment and selection process is one of the most crucial responsibilities of Human Resource Management. A well-structured process ensures that organizations attract, evaluate, and hire the right talent who not only have the required skills but also align with the company’s culture and long-term vision. From creating accurate job descriptions to onboarding new hires, every step contributes to building a strong workforce.
By following best practices—such as clear communication, fair evaluation, and effective onboarding—HR leaders can reduce turnover, improve employee satisfaction, and strengthen organizational growth. Ultimately, recruitment is not just about filling positions; it’s about investing in people who will drive success for the future.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between recruitment and selection?
Recruitment is about attracting candidates, while selection is about choosing the right one.
2. Why is recruitment and selection important in HR?
It ensures organizations hire skilled employees who contribute to business success.
3. What are common methods of recruitment?
Job portals, social media, employee referrals, campus placements, and recruitment agencies.
4. What are the main steps in selection?
Screening, interviews, assessments, background checks, and final offer.
5. How does technology help in recruitment and selection?
HR software and ATS streamline job posting, candidate tracking, resume screening, and interview scheduling.