Organizations typically rely on various sources of recruitment to fill available job positions across different departments. These sources not only inform potential candidates about job vacancies but also provide them with a way to connect and communicate with employers. By understanding and utilizing different recruitment sources, companies can significantly improve the efficiency and effectiveness of their hiring process.
The term “Source of Recruitment” refers to the specific channels or methods through which organizations identify, attract, and hire candidates. These sources can be internal (hiring from within the company) or external (hiring from outside). Each comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages, and choosing the right one can make or break the hiring process.

In this article, we’ll cover:
-
What is the source of recruitment?
-
The types of recruitment sources (internal and external)
-
Advantages and disadvantages of each type
-
Comparison between internal and external sources
-
Factors to consider when choosing the right source
-
Best practices to optimize recruitment sources
This blog will help HR professionals, managers, and students understand the complete picture of how organizations approach hiring and develop recruitment plans.
Key Takeaways
-
Organizations use both internal and external sources of recruitment to connect with suitable candidates, making the recruitment process more efficient.
-
Internal recruitment sources involve existing employees who can be promoted, transferred, or rehired. This method is cost-effective and time-efficient for organizations.
-
External recruitment sources refer to candidates outside the organization, offering the benefit of a larger talent pool and the infusion of new skills and fresh perspectives into the company.
What is Source of Recruitment?
A source of recruitment is a pathway used by companies to attract potential candidates for vacant job positions. These sources may vary depending on job requirements, organizational needs, budget, and industry trends.
Recruitment sources are broadly divided into two categories:
-
Internal Sources of Recruitment – filling vacancies from within the organization.
-
External Sources of Recruitment – hiring candidates from outside the organization.
The decision of which source to use depends on factors such as the urgency of hiring, skill requirements, cost, and long-term organizational goals.
Why Are Sources of Recruitment Important?
In Human Resource Management (HRM), the sources of recruitment play a crucial role in building a strong workforce. They determine not only how efficiently an organization fills vacancies but also the quality and long-term impact of its hires. Choosing the right recruitment sources can align hiring with business objectives, improve diversity, and enhance employee retention.
Here are the five key reasons why sources of recruitment are important:
1. Aligns with Business Hiring Goals
The sources of recruitment in HRM enable organizations to target the right candidates based on role type, urgency, and skill requirements. A robust recruitment source ensures that the selected candidates’ skills and expertise align with the company’s workforce planning and long-term growth strategy.
2. Influences Talent Reach and Diversity
Different sources of recruitment allow organizations to tap into a wide talent pool, ideal for meeting both immediate and future staffing needs. By leveraging diverse recruitment channels, companies can attract candidates from various backgrounds, industries, and locations—strengthening workplace diversity and inclusion.
3. Determines Hiring Speed and Volume
The choice of sources of recruitment and selection directly impacts the speed and scale of hiring. For instance, internal recruitment may speed up urgent hires, while external job portals and campus placements can help fill bulk positions within a short timeframe.
4. Impacts Candidate Experience
The source through which candidates discover job opportunities shapes their first impression of the organization. Professional, accessible, and engaging recruitment sources—such as well-designed career pages or social media job postings—enhance the candidate journey from initial contact to onboarding.
5. Affects Long-Term Employee Retention Rates
When top talent is sourced through the right channels, employees are more likely to feel aligned with organizational values and expectations. This increases job satisfaction and reduces turnover, contributing to a stable and high-performing workforce over time.
Types of Sources of Recruitment
Let’s explore the two major categories in detail:
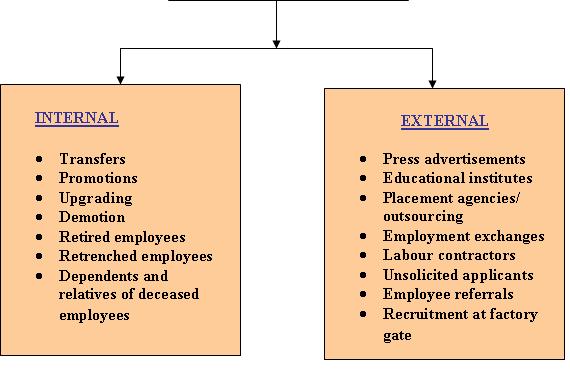
Internal Source of Recruitment:
Internal recruitment involves hiring candidates from within the organization. Persons who are already working in an Organization constitute the ‘internal sources’.
Retrenched employees, retired employees, dependents of deceased employees generally constitute the internal sources. Whenever any vacancy arises, someone from within the Organization is upgraded, transferred, promoted or even demoted.
Examples of Internal Source of Recruitment:
-
Promotions – Employees are elevated to higher roles based on performance and experience.
-
Transfers – Shifting employees from one department or location to another.
-
Employee Referrals – Current employees recommend potential candidates.
-
Re-employment of Former Employees – Hiring back ex-employees with proven skills.
-
Internal Job Postings – Vacancies are shared through company portals or notice boards.
Advantages of Internal Source of Recruitment:
-
Cost-Effective: Saves advertising and recruitment agency costs.
-
Time-Saving: Reduces the time taken to screen and hire.
-
Boosts Morale: Employees feel motivated when they see growth opportunities.
-
Better Cultural Fit: Internal candidates are already aligned with company values.
-
Lower Risk: Employers already know the candidate’s strengths and weaknesses.
Disadvantages of Internal Source of Recruitment:
-
Limited Talent Pool: Restricts hiring to existing employees only.
-
Stagnation: May reduce innovation and fresh ideas.
-
Employee Rivalry: Could create unhealthy competition among employees.
-
Role Vacancies: Promoting an employee may leave another role unfilled.
-
Favoritism: Risk of bias or favoritism in promotions and transfers.
2. External Sources of Recruitment
External recruitment means attracting candidates from outside the organization. This approach is commonly used when companies need fresh talent, specialized skills, or a larger pool of applicants.
- Employees working in other Organizations
- Job aspirants registered with employment exchanges
- Students from reputed educational institutions
- Candidates referred by unions, friends, relatives and existing employees
- Candidates forwarded by search firms and contractors
- Candidates responding to the advertisements, issued by the Organization; and
- Unsolicited applications/ walk-Ins
Examples of External Source of Recruitment:
-
Online Job Portals: Websites like Naukri, Indeed, and Glassdoor.
-
Recruitment Agencies: Professional consultancies that source candidates.
-
Campus Recruitment: Hiring fresh graduates from universities and colleges.
-
Job Fairs: Events where companies connect with potential candidates.
-
Social Media Recruitment: Platforms like LinkedIn, Facebook, and Instagram.
-
Walk-in Interviews: Open interviews for large-scale hiring.
-
Employee Poaching: Recruiting talent from competitor companies.
Advantages of External Source of Recruitment:
-
Wider Talent Pool: Access to a larger and more diverse set of candidates.
-
Fresh Ideas: New employees bring innovation and different perspectives.
-
Specialized Skills: External hiring helps find candidates with niche expertise.
-
Competitive Advantage: Hiring from outside can strengthen the company’s market position.
-
Diversity and Inclusion: Helps in building a more inclusive workforce.
Disadvantages of External Source of Recruitment:
-
High Cost: Advertising, job portals, and agency fees can be expensive.
-
Time-Consuming: Screening, interviewing, and onboarding take longer.
-
Cultural Adjustment: New hires may take time to adapt to company culture.
-
Higher Attrition Risk: External recruits may leave if expectations aren’t met.
-
Uncertainty: Employers may not fully know the candidate’s work ethics or loyalty.
Internal vs External Sources of Recruitment
Here’s a quick comparison to help you understand the difference:
| Factor | Internal Sources | External Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Low | High |
| Time | Faster hiring process | Slower and more complex |
| Talent Pool | Limited to existing employees | Wider and more diverse |
| Employee Morale | Boosts motivation and loyalty | May cause dissatisfaction in current staff |
| Innovation | Limited fresh ideas | Brings creativity and new perspectives |
| Risk | Lower (candidate already known) | Higher (uncertainty in behavior/per |
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Source of Recruitment
HR managers should carefully evaluate these factors before finalizing a recruitment source:
-
Nature of the Job: Technical jobs may require external hiring, while managerial roles may favor internal promotions.
-
Budget Constraints: Internal hiring is cost-effective, whereas external hiring may require a bigger budget.
-
Urgency of Hiring: If speed is crucial, internal recruitment is faster.
-
Long-Term Goals: For innovation and diversity, external sources are better.
-
Availability of Skills: If skills are not available internally, external recruitment is necessary.
Things to Consider When Choosing an Internal Source of Recruitment
An internal source of recruitment refers to filling job vacancies with existing employees through promotions, transfers, or internal job postings. This method saves time and costs while boosting employee loyalty. However, it also comes with challenges that HR managers should carefully evaluate before relying solely on internal hiring.
Here are the important considerations when choosing an internal source of recruitment:
-
Limited Skills Pool
-
Internal hiring restricts the search to current employees, which may limit access to fresh skills and innovative perspectives.
-
This can become a challenge for highly technical or specialized roles.
-
-
Reduced Diversity
-
Depending only on internal recruitment may prevent the company from gaining diverse ideas, experiences, and cultural perspectives that come with external hires.
-
-
Impact on Employee Morale
-
While promotions motivate employees, not everyone can be promoted at once.
-
Employees who are passed over may feel demotivated or undervalued.
-
-
Workplace Tension
-
Internal competition for promotions or transfers can create rivalry and conflict among employees, potentially affecting teamwork.
-
-
Nepotism and Bias
-
Employees might recommend friends or family members, leading to favoritism.
-
This can result in less qualified individuals being selected for roles.
-
-
Skill Gaps
-
Even though internal candidates may understand the company culture, they might lack the specific expertise required for a new role.
-
Training and upskilling become crucial in such cases.
-
✅ Summary:
An internal source of recruitment is cost-effective and time-saving while also improving retention and employee morale. However, HR managers must be mindful of its limitations, such as skill gaps, restricted diversity, and potential conflicts. A balanced approach that combines internal growth opportunities with external talent acquisition works best for long-term organizational success.
Things to Consider When Choosing an External Source of Recruitment
An external source of recruitment allows organizations to bring in fresh talent, new perspectives, and specialized skills from outside the company. While it broadens the talent pool, it also requires time, cost, and cultural adjustments. HR managers must carefully weigh these factors before deciding to hire externally.
Here are the key considerations when using an external source of recruitment:
-
Time Efficiency
-
Hiring externally often takes longer due to job postings, application screening, interviews, and background checks.
-
This may delay filling urgent roles, so companies should plan accordingly.
-
-
Training and Onboarding
-
New hires from outside may not be familiar with the company’s culture, policies, or processes.
-
A strong onboarding and training program is essential to ensure smooth integration.
-
-
Employee Morale
-
Promoting outsiders over existing employees can sometimes discourage internal staff.
-
Employees may feel overlooked for promotions or career advancement opportunities.
-
-
Workplace Tension
-
Introducing new employees may create competition or tension between existing and new staff.
-
This could impact teamwork and overall productivity if not managed well.
-
-
Cultural Adjustment
-
External hires may struggle to adapt to the company’s culture or working style.
-
Without proper support, this can lead to poor retention rates and higher turnover.
-
-
Cost Implications
-
External recruitment usually involves higher expenses—advertisements, recruitment agencies, job fairs, or online job boards.
-
Organizations must evaluate whether the long-term benefits justify the additional cost.
-
✅ Summary:
An external source of recruitment offers organizations the chance to access a wider and more diverse pool of candidates, but it comes with challenges such as higher costs, longer timelines, and cultural adaptation needs. By planning carefully and balancing external recruitment with internal growth opportunities, companies can maximize the benefits while reducing risks.
Best Practices for Effective Recruitment Sources
To optimize the use of recruitment sources, companies should follow these best practices:
-
Use a Balanced Approach: Combine both internal and external recruitment based on role requirements.
-
Leverage Technology: Use Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS) and AI-driven tools for efficiency.
-
Build an Employer Brand: Strong branding attracts top talent through both internal and external sources.
-
Encourage Employee Referrals: They are cost-effective and bring in trusted candidates.
-
Track Recruitment Metrics: Monitor cost-per-hire, time-to-fill, and quality of hire to improve processes.
-
Focus on Diversity and Inclusion: Use external sources to create a diverse workforce.
-
Regularly Update Job Portals and Social Media: Active presence improves candidate reach.
Case Study: Balancing Internal and External Recruitment
Consider a multinational IT company hiring for a Project Manager role.
-
For internal recruitment, they evaluate senior team leads who already know the company’s processes. This boosts employee morale and saves training costs.
-
For external recruitment, they also advertise the role on LinkedIn and engage recruitment agencies to attract professionals with global project management experience.
The company ultimately chooses a hybrid approach – promoting one internal employee to a managerial role while hiring externally for a specialized technical position. This balance ensures growth opportunities for employees while also introducing fresh talent into the organization.
Conclusion
The sources of recruitment form the foundation of an effective hiring process. By understanding the types—internal sources such as promotions, transfers, and referrals, and external sources like job portals, social media, and campus hiring—organizations can make better decisions to meet both short-term staffing needs and long-term strategic goals.
While internal sources provide cost savings, speed, and employee motivation, external sources bring fresh talent, diverse perspectives, and specialized skills. Each has its advantages and challenges, but the key to successful recruitment lies in balancing both approaches based on the role, urgency, and organizational objectives.
Ultimately, choosing the right source of recruitment not only impacts hiring efficiency but also shapes the quality of talent, employee retention, and business growth. For HR professionals, mastering recruitment sources is essential to building a strong, high-performing workforce.
FAQs on Sources of Recruitment
1. What is the source of recruitment in HRM?
The source of recruitment refers to the method or channel through which organizations identify, attract, and hire candidates. It includes internal sources (within the company) and external sources (outside the company).
2. What are the main types of sources of recruitment?
The two main types are:
-
Internal Sources – Promotions, transfers, employee referrals, and re-employment of ex-employees.
-
External Sources – Job portals, recruitment agencies, campus placements, job fairs, and social media.
3. Why are sources of recruitment important?
They are important because they align hiring with business goals, improve diversity, determine hiring speed and efficiency, shape candidate experience, and influence long-term employee retention.
4. What are the advantages of internal sources of recruitment?
Internal sources are cost-effective, time-saving, motivate employees, reduce training needs, and lower hiring risks since candidates are already familiar with the organization.
5. What are the disadvantages of external sources of recruitment?
External recruitment can be costly, time-consuming, and carries higher risks of cultural mismatch or attrition. It also requires additional training and onboarding for new hires.
6. How should organizations choose the right source of recruitment?
Companies should consider factors like the nature of the job, urgency, budget, availability of skills, and long-term workforce goals when choosing between internal and external sources.